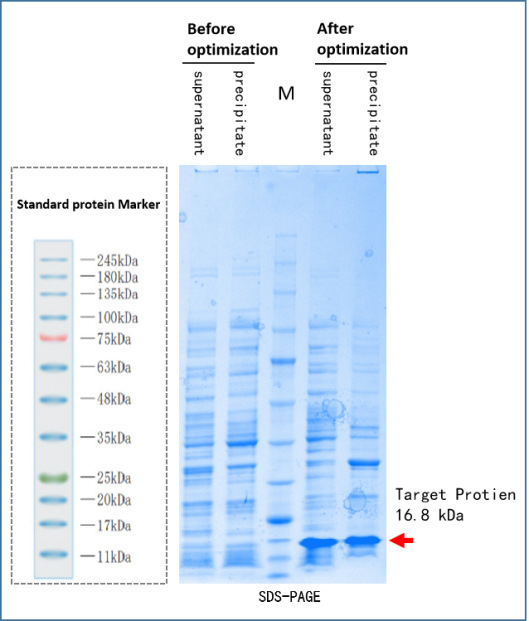
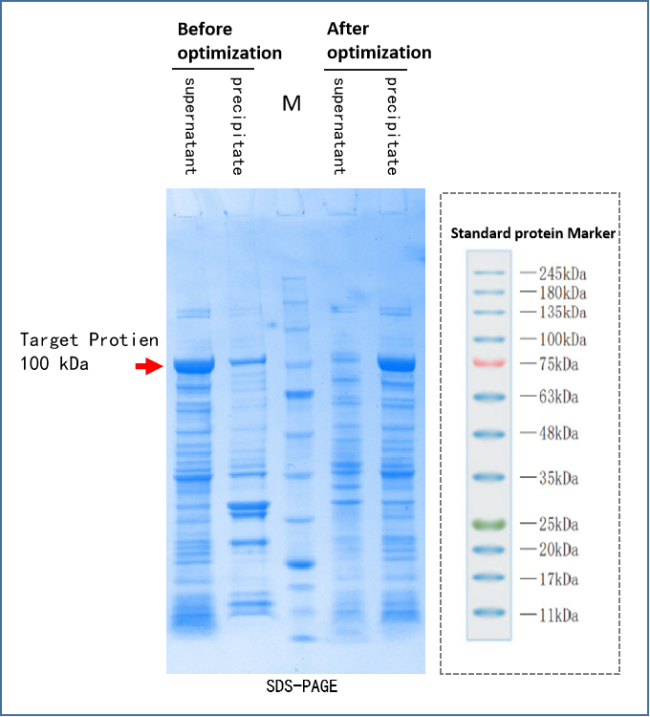
High and low GC content, repetitive sequence:
Solution: Divide the sequence into small segments to reduce the impact of structure, and choose the optimal connection solution, such as enzyme digestion and ligation and multi-segment recombination.
Long sequences
Solution: use multi-segment recombination to construct divided gene fragments, and combine them with vitro and vivo assembly.
Special parts of vectors (e.g. ccdB, LTR)
Solution: Use different competent cells corresponding to different parts of vectors, such as DB3.1, which renders the strain resistant to the toxic effects of the ccdB gene, the recombination-deficient Stbl series, etc.
Other unpredictable difficulties, such as genetic instability and toxicity, and the introduction of random mutations and deletions
Solution: Try different competent cells.